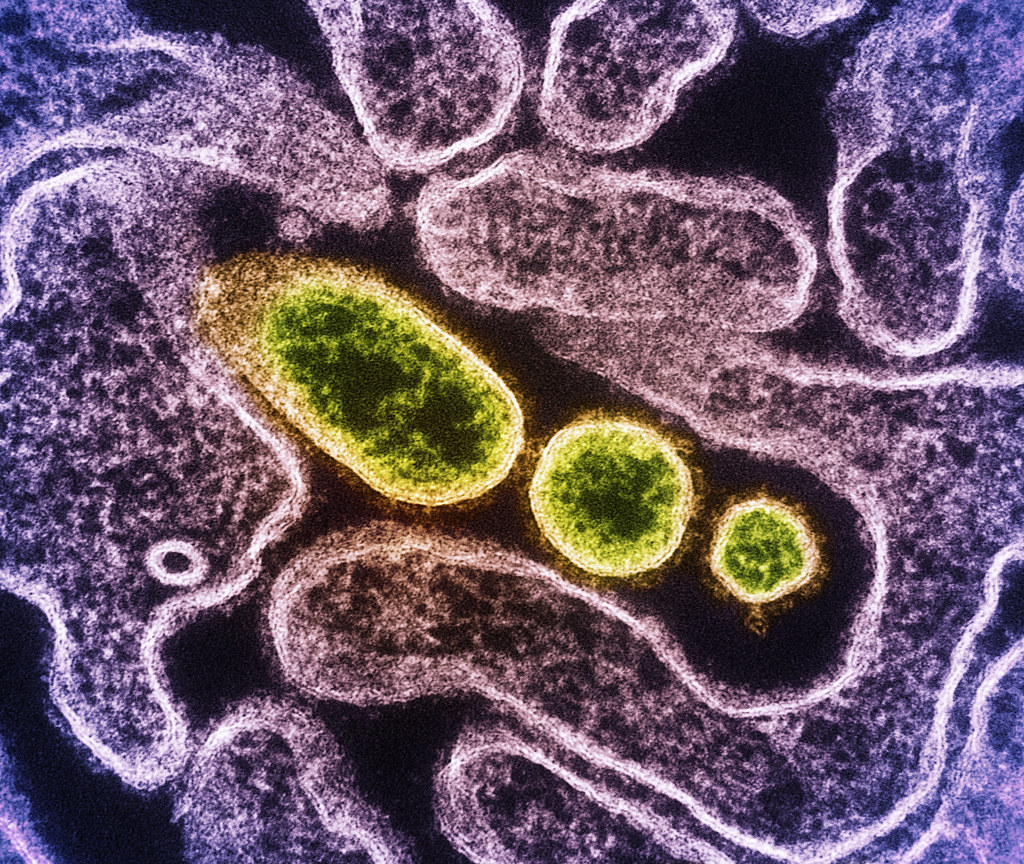
Overview
What is the Nipah virus?
The Nipah virus is a zoonotic virus that was first identified in Malaysia in 1999. It is primarily transmitted from animals to humans, although human-to-human transmission has also been reported. The virus belongs to the family Paramyxoviridae and is classified as a biosafety level 4 (BSL-4) pathogen, meaning it poses a high risk to human health and requires strict containment measures. Nipah virus infection can cause a range of symptoms, including fever, headache, dizziness, respiratory distress, and encephalitis. In severe cases, it can lead to coma and death. There is currently no specific treatment or vaccine for Nipah virus infection, and management focuses on supportive care and prevention of transmission.
History of the Nipah virus
The Nipah virus, first identified in 1999 in Malaysia, is a zoonotic virus that is transmitted from animals to humans. The virus is primarily found in fruit bats of the Pteropodidae family, but it can also be transmitted through contact with infected pigs or consumption of contaminated food. The initial outbreak of the Nipah virus resulted in severe respiratory illness and encephalitis in humans, with a high mortality rate. Since then, several outbreaks of the Nipah virus have occurred in different parts of the world, highlighting the need for continued surveillance and research to prevent future outbreaks and develop effective treatments.
Transmission of the Nipah virus
The Nipah virus is primarily transmitted to humans through direct contact with infected bats or pigs. The virus can also be transmitted from person to person through close contact, such as caring for an infected individual or through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Additionally, consuming fruits or fruit products contaminated with the virus can also lead to transmission. It is important to practice good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly and avoiding contact with sick individuals or animals, to reduce the risk of transmission.
Symptoms
Initial symptoms
The initial symptoms of the Nipah virus infection are similar to those of a common cold or flu. These symptoms include fever, headache, muscle pain, sore throat, and fatigue. However, as the infection progresses, more severe symptoms may develop, such as respiratory problems, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), and seizures. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, especially if you have been in an area where the Nipah virus is known to occur.
Progression of symptoms
The progression of symptoms in Nipah virus infection can vary from person to person. Typically, the initial symptoms include fever, headache, and muscle pain. As the infection progresses, individuals may experience dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and respiratory problems. In severe cases, Nipah virus infection can lead to encephalitis, characterized by inflammation of the brain, which can cause seizures, confusion, and even coma. It is important to seek medical attention if any symptoms of Nipah virus infection are observed, as early diagnosis and treatment can improve the chances of recovery.
Severe symptoms
Severe symptoms of the Nipah virus infection can be extremely debilitating and life-threatening. These symptoms include high fever, severe headache, dizziness, and confusion. Patients may also experience respiratory distress, with difficulty breathing and coughing. In some cases, the infection can lead to encephalitis, causing inflammation of the brain and potentially leading to seizures and coma. It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if any of these severe symptoms are present, as early intervention can greatly improve the chances of recovery.
Diagnosis
Clinical evaluation
Clinical evaluation is an important step in diagnosing and understanding the Nipah virus. It involves a thorough examination of the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and laboratory tests. During the clinical evaluation, healthcare professionals look for specific signs and symptoms such as fever, headache, respiratory distress, and encephalitis. They also assess the patient’s exposure to potential sources of the virus, such as contact with infected animals or consumption of contaminated food. Additionally, laboratory tests, including blood tests and imaging studies, may be conducted to confirm the presence of the Nipah virus. The information gathered during the clinical evaluation helps healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis and determine the appropriate course of treatment for the patient.
Laboratory tests
Laboratory tests are essential in diagnosing the Nipah virus. These tests involve the analysis of blood, urine, and respiratory samples to detect the presence of the virus or its antibodies. The most common laboratory tests for Nipah virus include polymerase chain reaction (PCR), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and virus isolation. PCR is used to amplify and detect the genetic material of the virus, while ELISA is used to detect antibodies produced by the immune system in response to the infection. Virus isolation involves growing the virus in a laboratory setting to confirm its presence. These laboratory tests play a crucial role in identifying and confirming Nipah virus infections, allowing for appropriate treatment and prevention measures to be implemented.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for Nipah virus includes other viral infections such as influenza, dengue fever, and Japanese encephalitis. These infections can present with similar symptoms like fever, headache, and respiratory distress. However, Nipah virus is characterized by its ability to cause severe neurological symptoms, including encephalitis, seizures, and coma. Laboratory tests, including PCR and serology, can help differentiate Nipah virus from other viral infections. Early diagnosis is crucial for appropriate management and containment of the disease.
Treatment
Supportive care
Supportive care is an essential aspect of managing patients with Nipah virus infection. The primary goal of supportive care is to alleviate symptoms and provide comfort to the patient. This includes measures such as maintaining hydration, managing fever, and providing respiratory support if necessary. Additionally, close monitoring of vital signs and organ function is crucial to ensure timely intervention in case of any complications. Supportive care plays a vital role in improving patient outcomes and reducing the risk of complications associated with Nipah virus infection.
Antiviral medications
Antiviral medications are an important aspect of treating the Nipah virus. These medications work by inhibiting the replication of the virus, helping to reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. While there is currently no specific antiviral medication approved for the treatment of Nipah virus infection, several broad-spectrum antiviral drugs have shown promise in laboratory studies. These drugs target the viral enzymes and proteins involved in viral replication, preventing the virus from spreading and causing further damage. However, it is important to note that the effectiveness of antiviral medications may vary depending on the individual and the stage of the infection. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment options and guidance.
Experimental treatments
Experimental treatments for Nipah virus are still in the early stages of development. Currently, there is no specific antiviral medication or vaccine available for Nipah virus. However, researchers are exploring various experimental treatments, such as monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs, to combat the virus. These treatments aim to target the virus and prevent it from replicating in the body. While these experimental treatments show promise, more research and clinical trials are needed to determine their effectiveness and safety in treating Nipah virus infections.
Prevention
Personal hygiene
Personal hygiene plays a crucial role in preventing the spread of the Nipah virus. It is important to regularly wash hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after coming into contact with potentially contaminated surfaces or objects. Additionally, covering the mouth and nose with a tissue or elbow when coughing or sneezing can help prevent the transmission of the virus. Avoiding close contact with individuals who are showing symptoms of the Nipah virus, such as fever, cough, and respiratory distress, is also essential. By practicing good personal hygiene habits, individuals can reduce their risk of contracting and spreading the Nipah virus.
Avoiding contact with infected animals
To avoid contact with infected animals, it is important to practice good hygiene and take necessary precautions. This includes avoiding direct contact with bats, pigs, or any other animals that may be carriers of the Nipah virus. It is also recommended to avoid consuming raw fruits or vegetables that may have been contaminated by bats or other infected animals. Additionally, it is crucial to follow proper handwashing techniques and use hand sanitizers regularly. By taking these preventive measures, the risk of contracting the Nipah virus can be significantly reduced.
Vaccination
Vaccination plays a crucial role in preventing the spread of the Nipah virus. Currently, there is no specific vaccine available for Nipah virus infection. However, efforts are underway to develop a vaccine that can provide protection against this deadly virus. In the meantime, it is important to follow preventive measures such as practicing good hygiene, avoiding contact with infected individuals, and staying away from areas with reported cases of Nipah virus. By taking these precautions, we can reduce the risk of contracting the virus and help in controlling its spread.
Conclusion
Summary of key points
The Nipah virus is a zoonotic virus that causes severe respiratory illness in humans. It was first identified in Malaysia in 1999 during an outbreak among pig farmers. The virus is primarily transmitted from animals to humans through direct contact with infected bats or pigs. The symptoms of Nipah virus infection include fever, headache, dizziness, and respiratory distress. In severe cases, it can lead to encephalitis, characterized by inflammation of the brain. There is currently no specific treatment for Nipah virus infection, and prevention measures focus on avoiding contact with infected animals and practicing good hygiene.
Importance of early detection
Early detection of the Nipah virus is crucial for preventing its spread and minimizing its impact on individuals and communities. By identifying and diagnosing cases of Nipah virus infection as early as possible, healthcare professionals can initiate appropriate treatment and implement necessary control measures to prevent further transmission. Early detection also allows for timely public health interventions, such as contact tracing and quarantine, which are essential for containing the spread of the virus. Moreover, early detection can help raise awareness among the public and promote preventive measures, such as practicing good hygiene and avoiding contact with infected individuals or animals. Overall, the importance of early detection in managing the Nipah virus cannot be overstated, as it plays a vital role in safeguarding public health and mitigating the impact of this potentially deadly disease.
Future research directions
Future research directions in the field of Nipah virus should focus on several key areas. Firstly, there is a need for further study into the transmission dynamics of the virus, including the identification of potential intermediate hosts and the routes of transmission to humans. Secondly, efforts should be made to develop effective antiviral therapies and vaccines to prevent and treat Nipah virus infections. Additionally, research should be conducted to better understand the pathogenesis of the virus and its impact on different organ systems. Furthermore, surveillance and early detection systems should be strengthened to enable timely response and containment of outbreaks. Lastly, collaborative research efforts between different countries and organizations should be promoted to enhance knowledge sharing and coordination in the fight against Nipah virus.